Golang Tips
Contents
Golang Programming 教学视频截图
Bits
Bit 图解
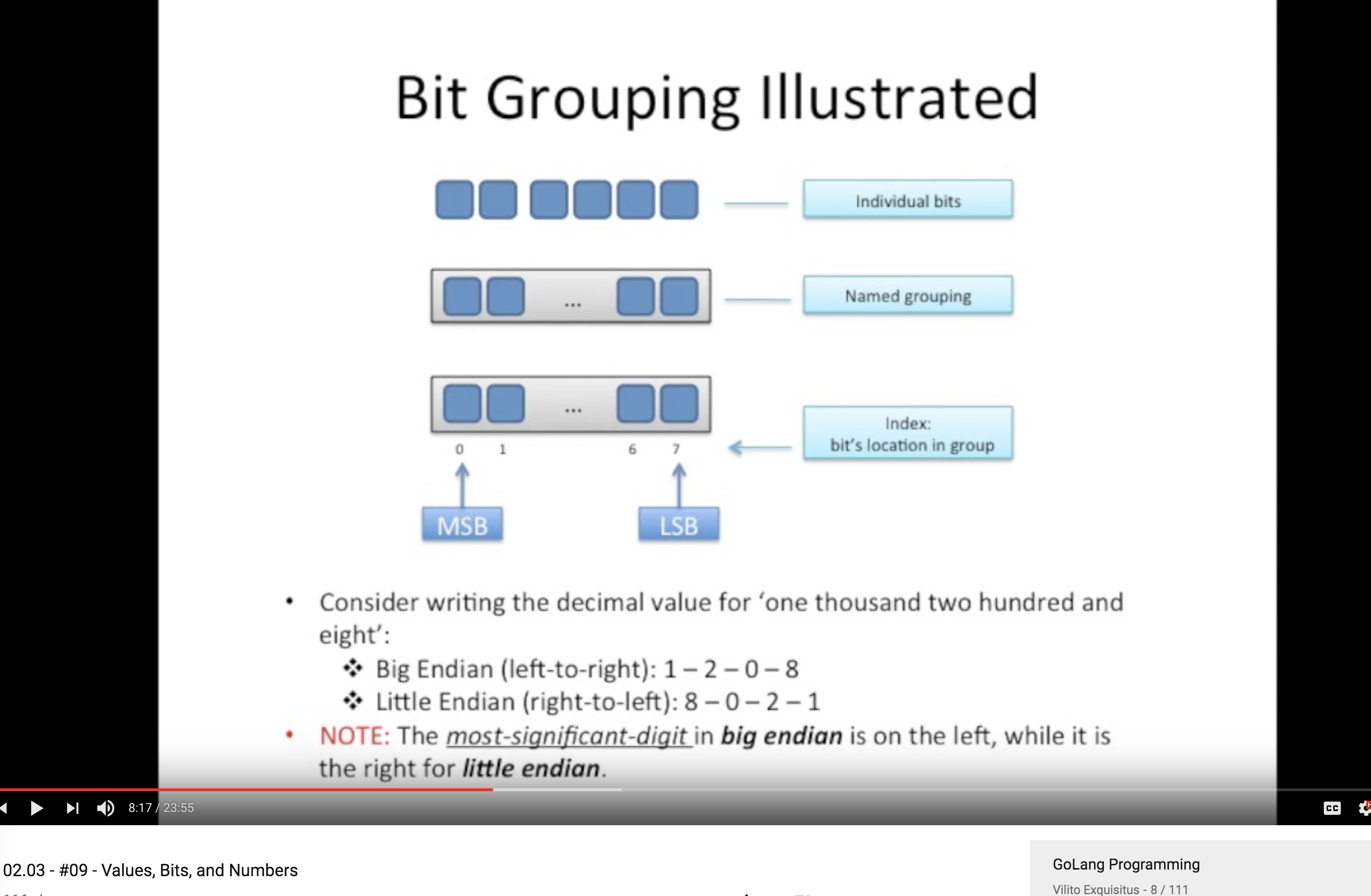
Bits 分组
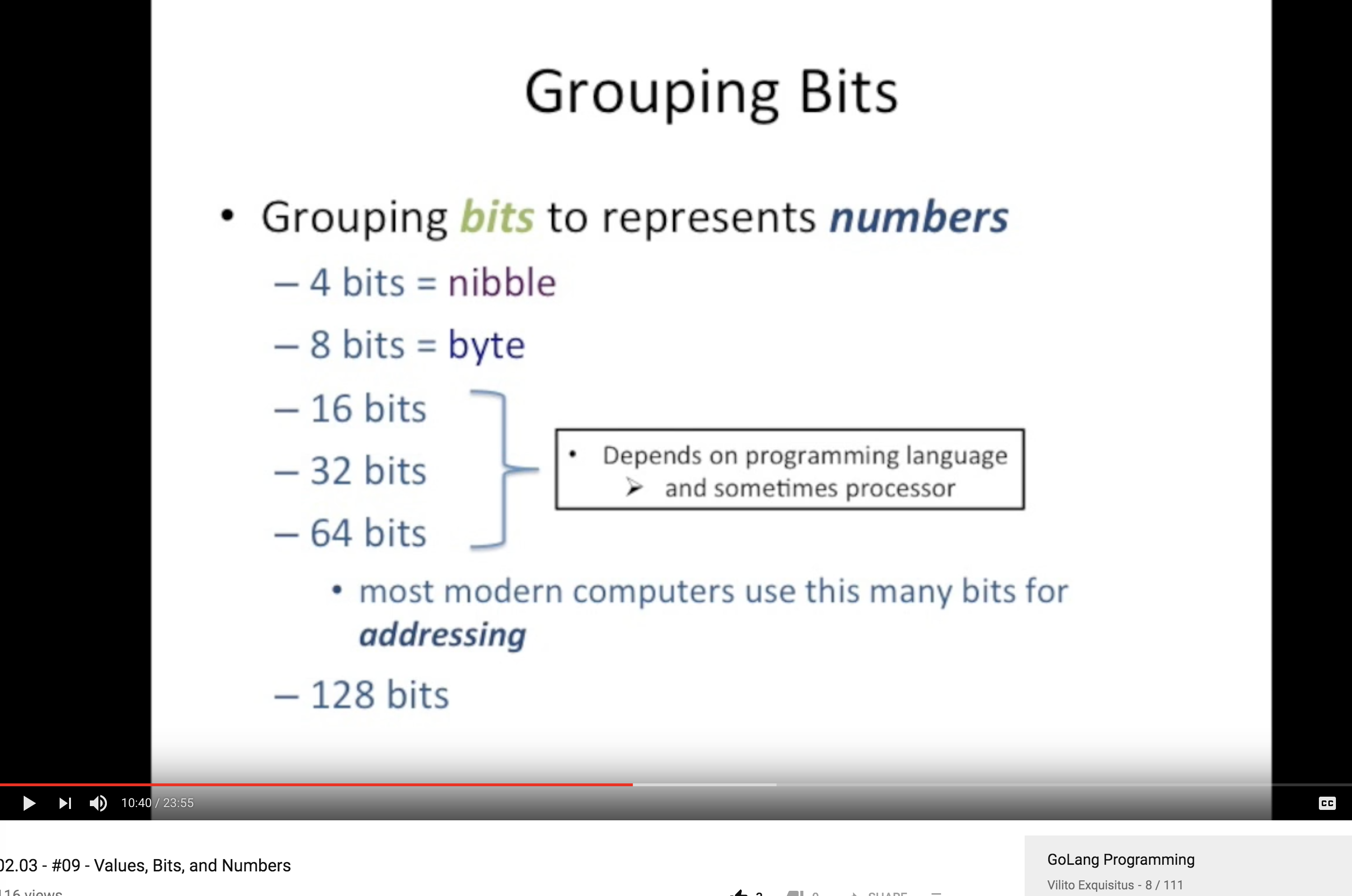
Binary Number

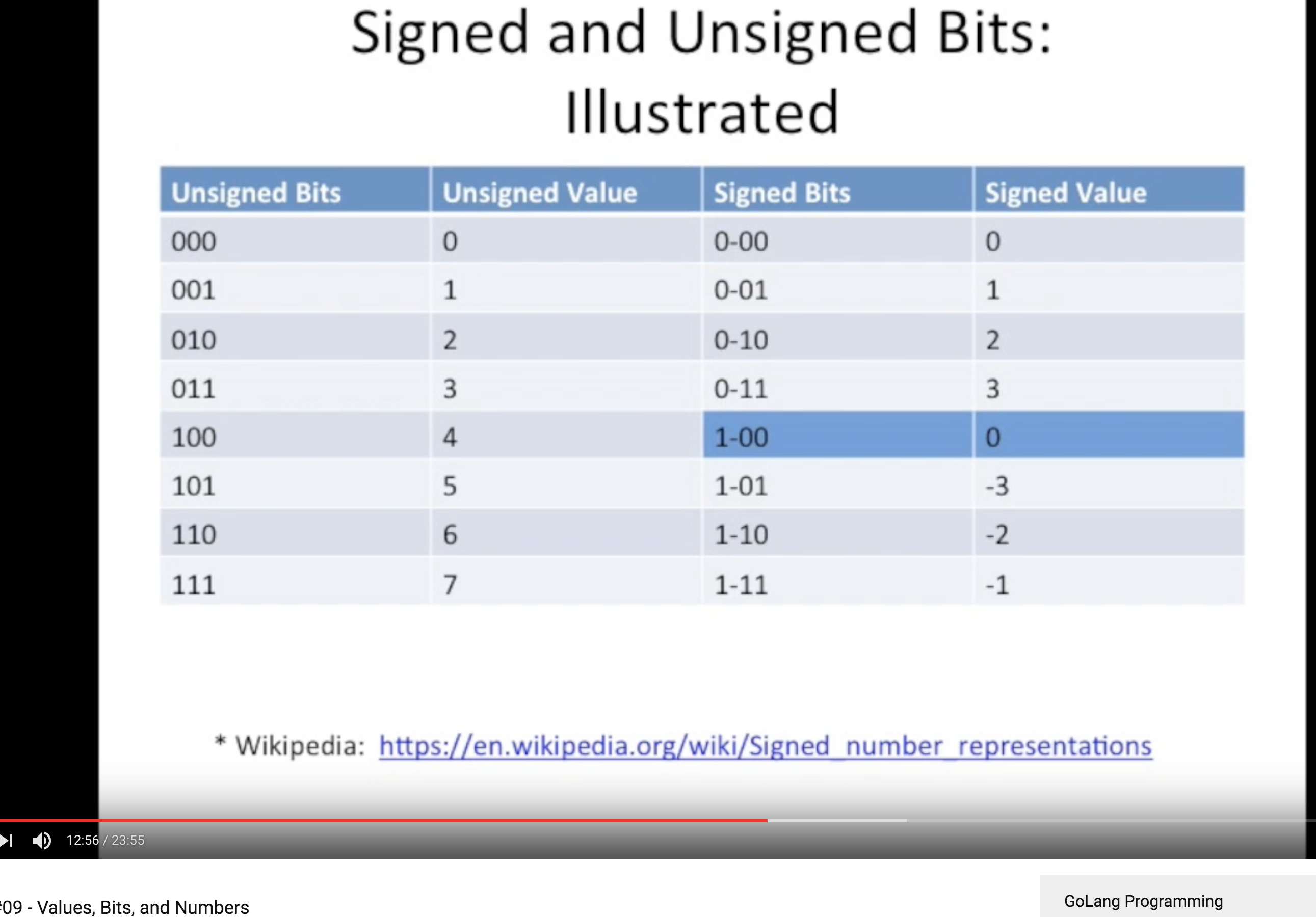
Signed & Unsigned Bits

Signed vs Unsigned Bits
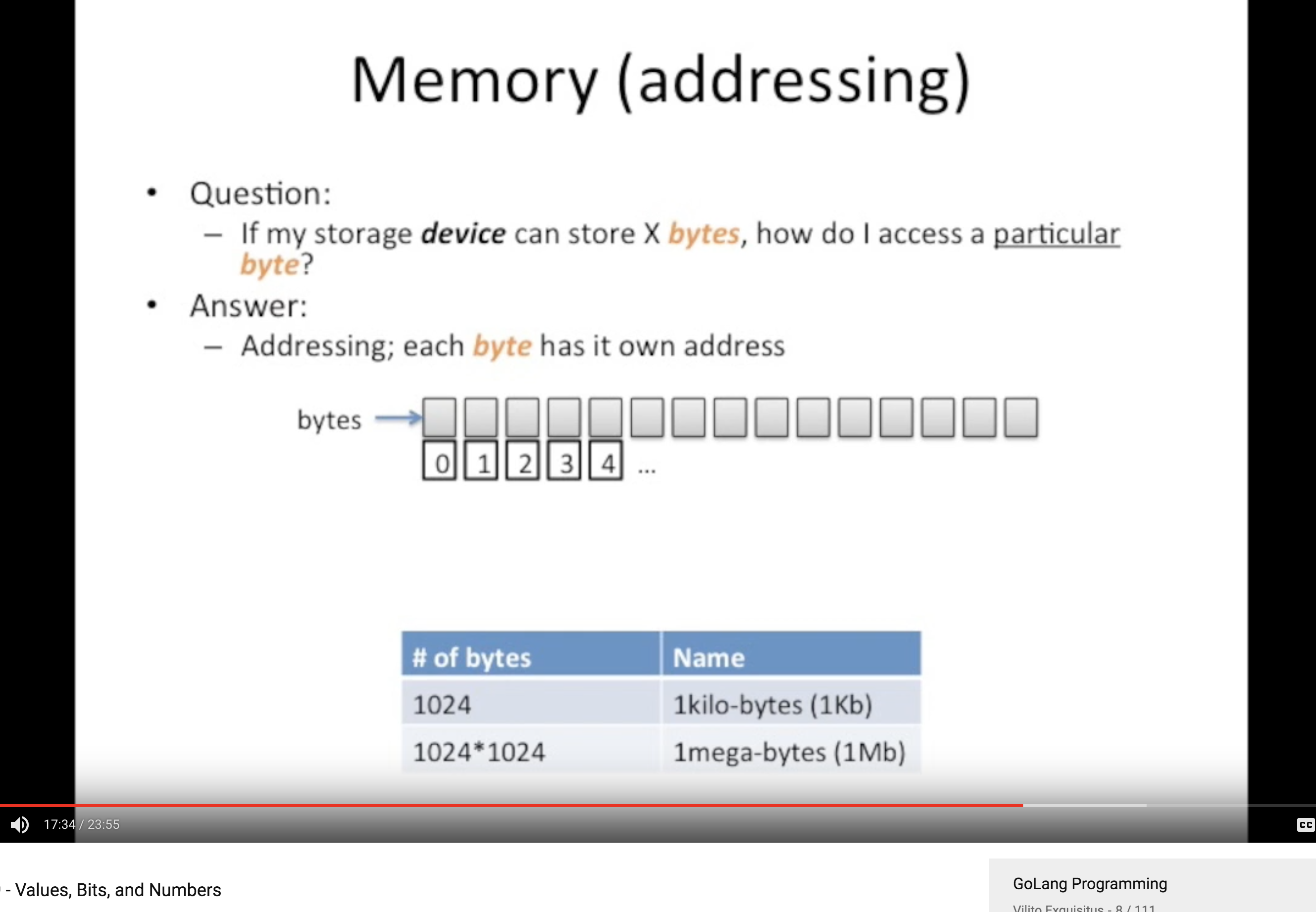
Bits in Memory
Memory Address
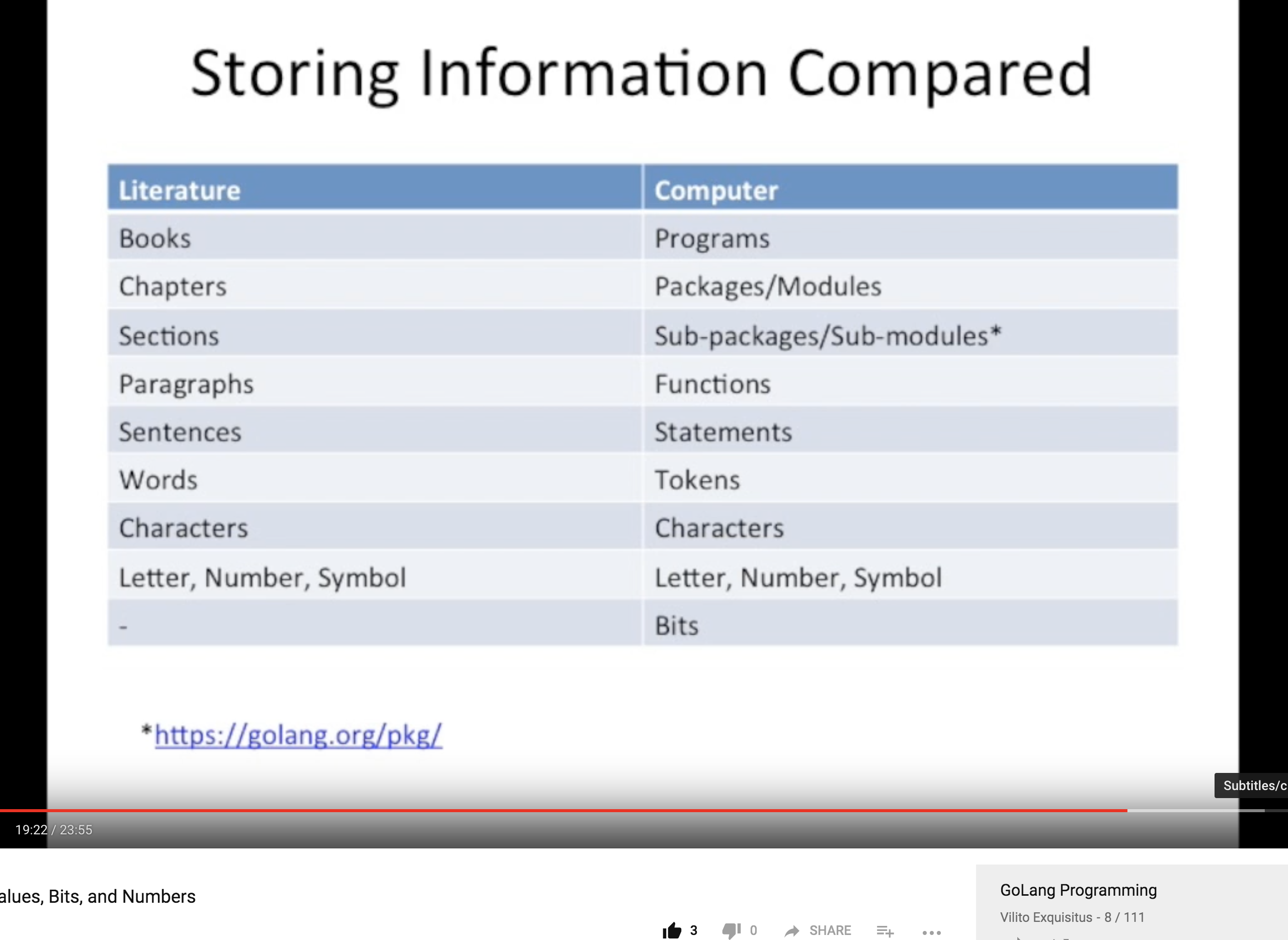
Book vs Computer 信息存储
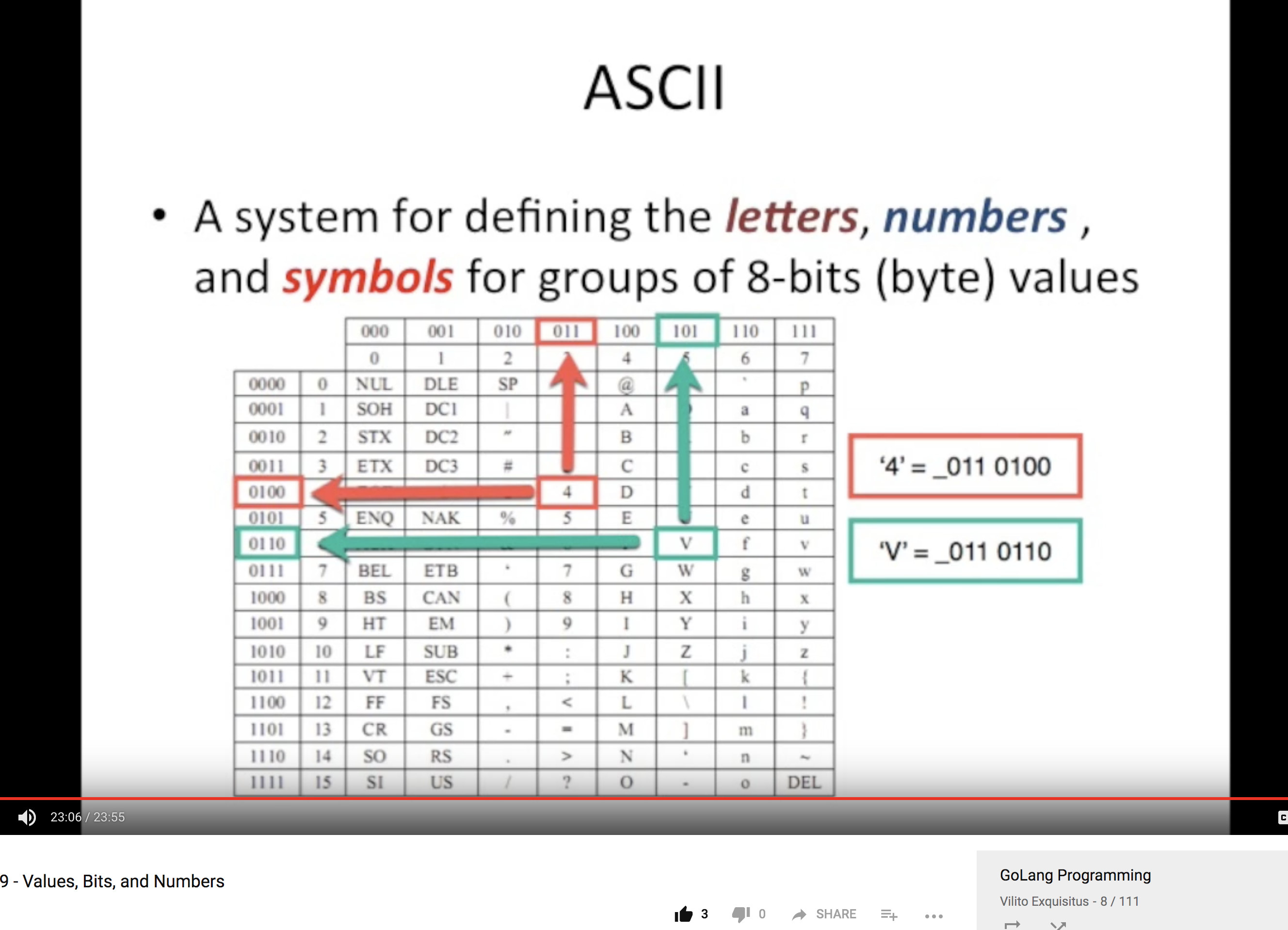
ASCII
Data Type
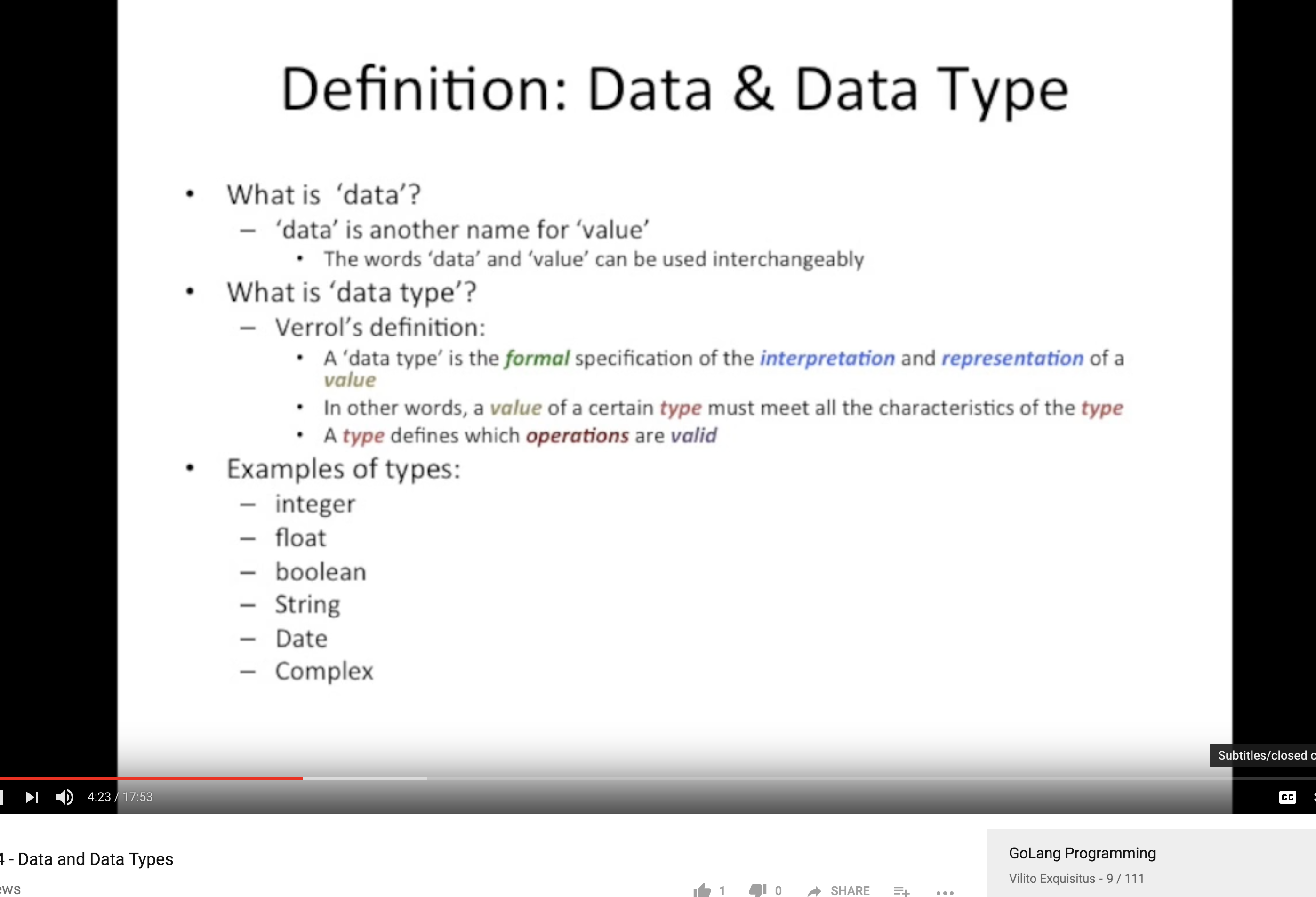
Data & Data Type
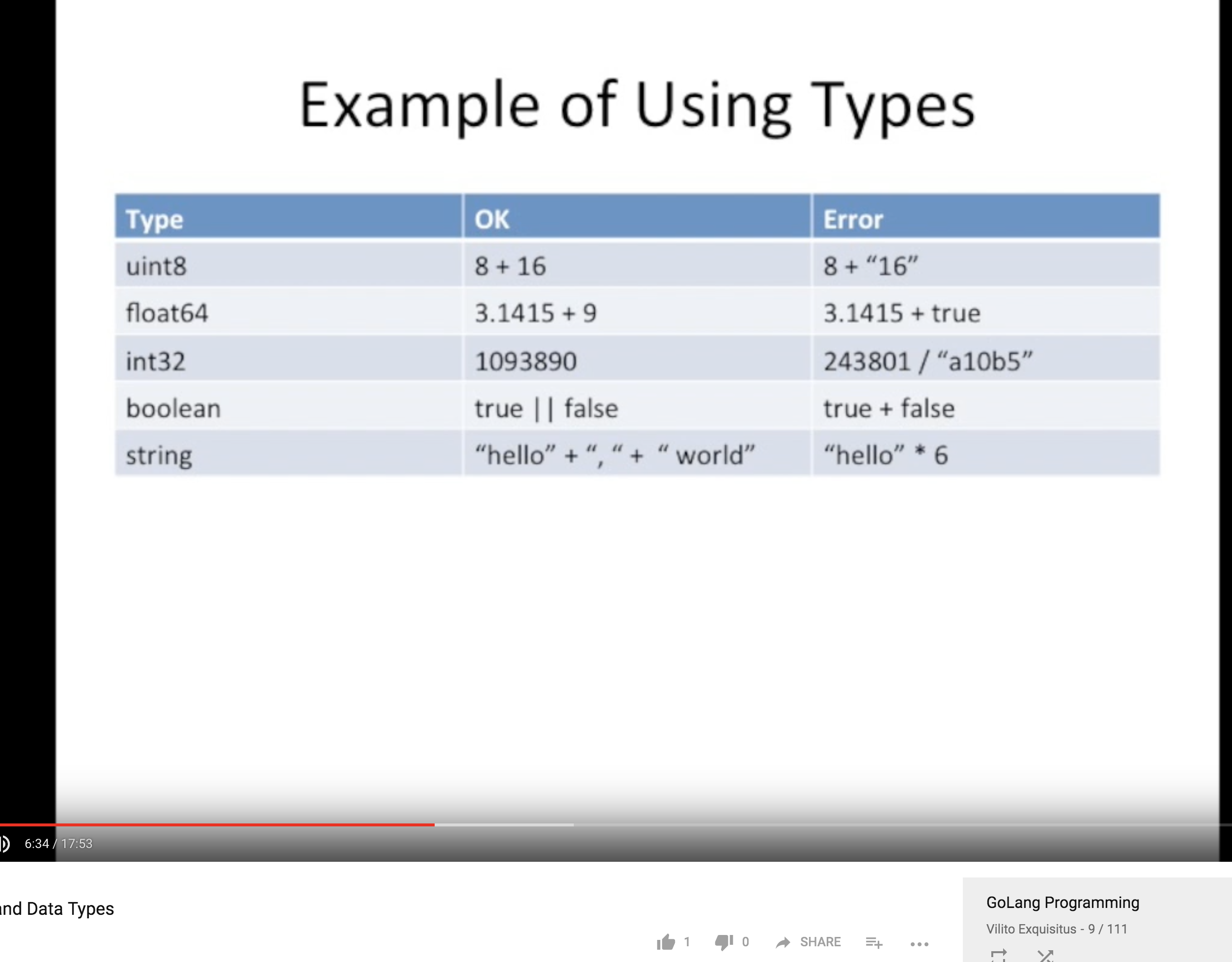
Type 的使用
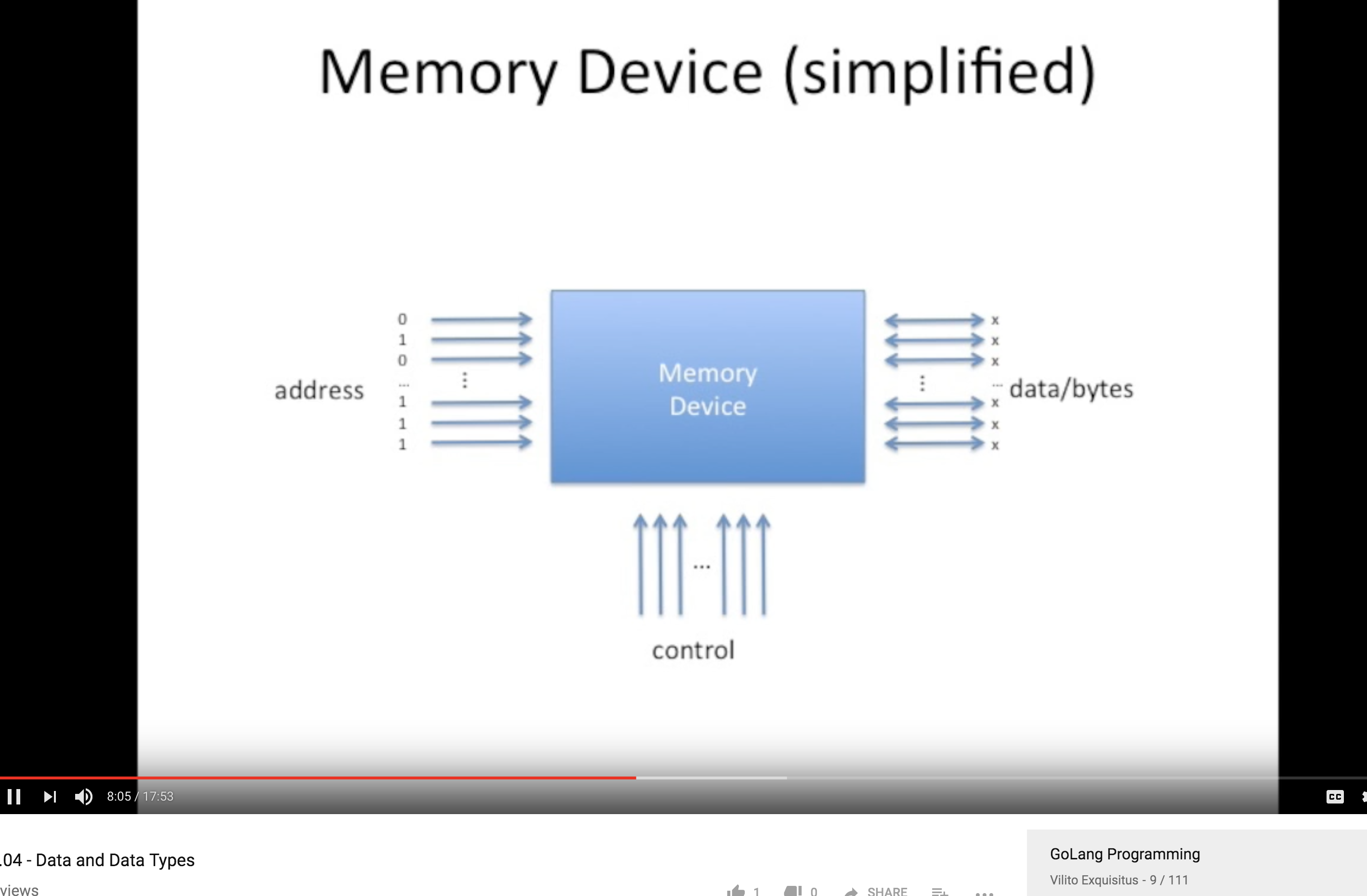
Memory 设备
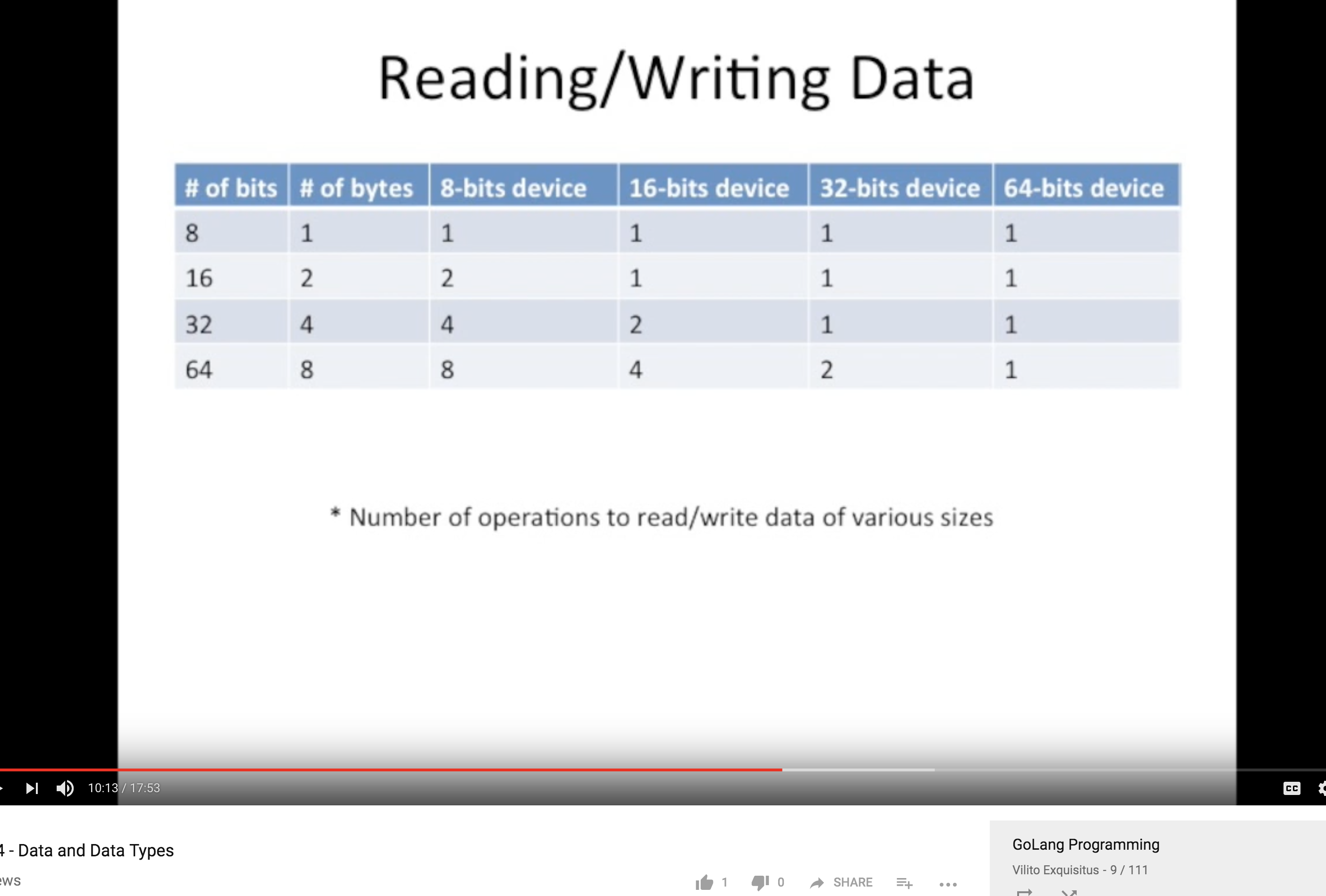
Data 读写
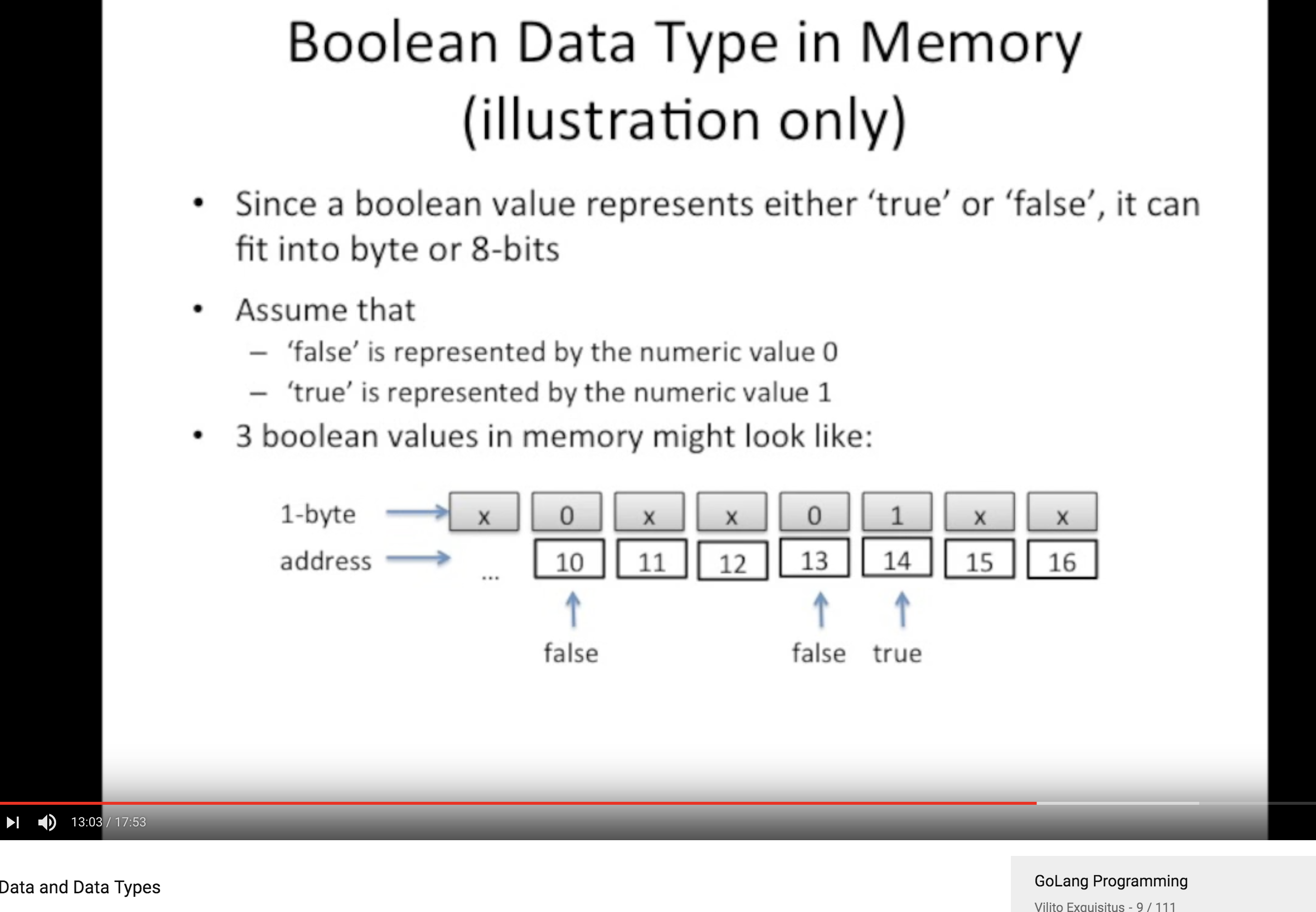
Boolean 类型
Integer 类型
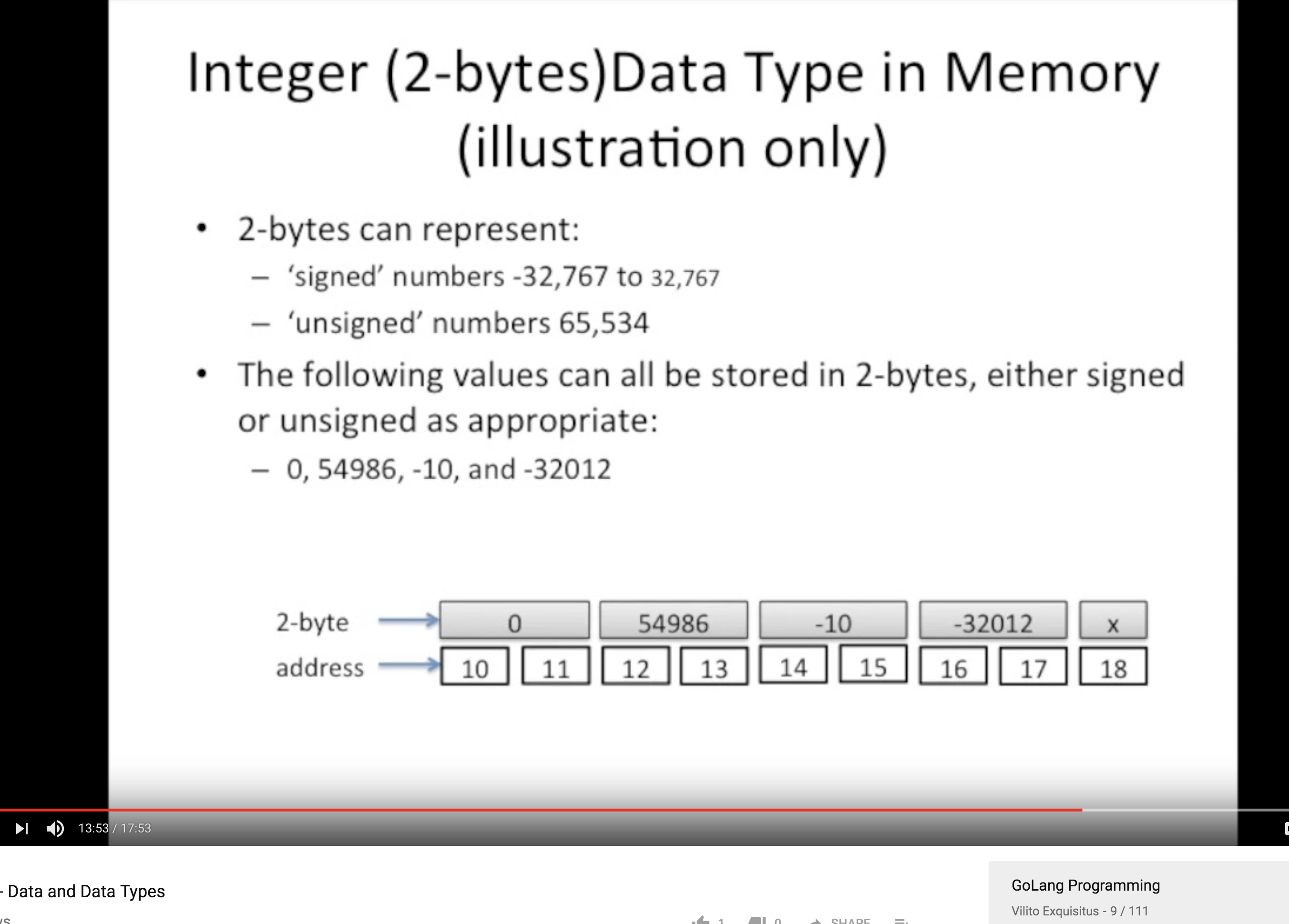
String 类型
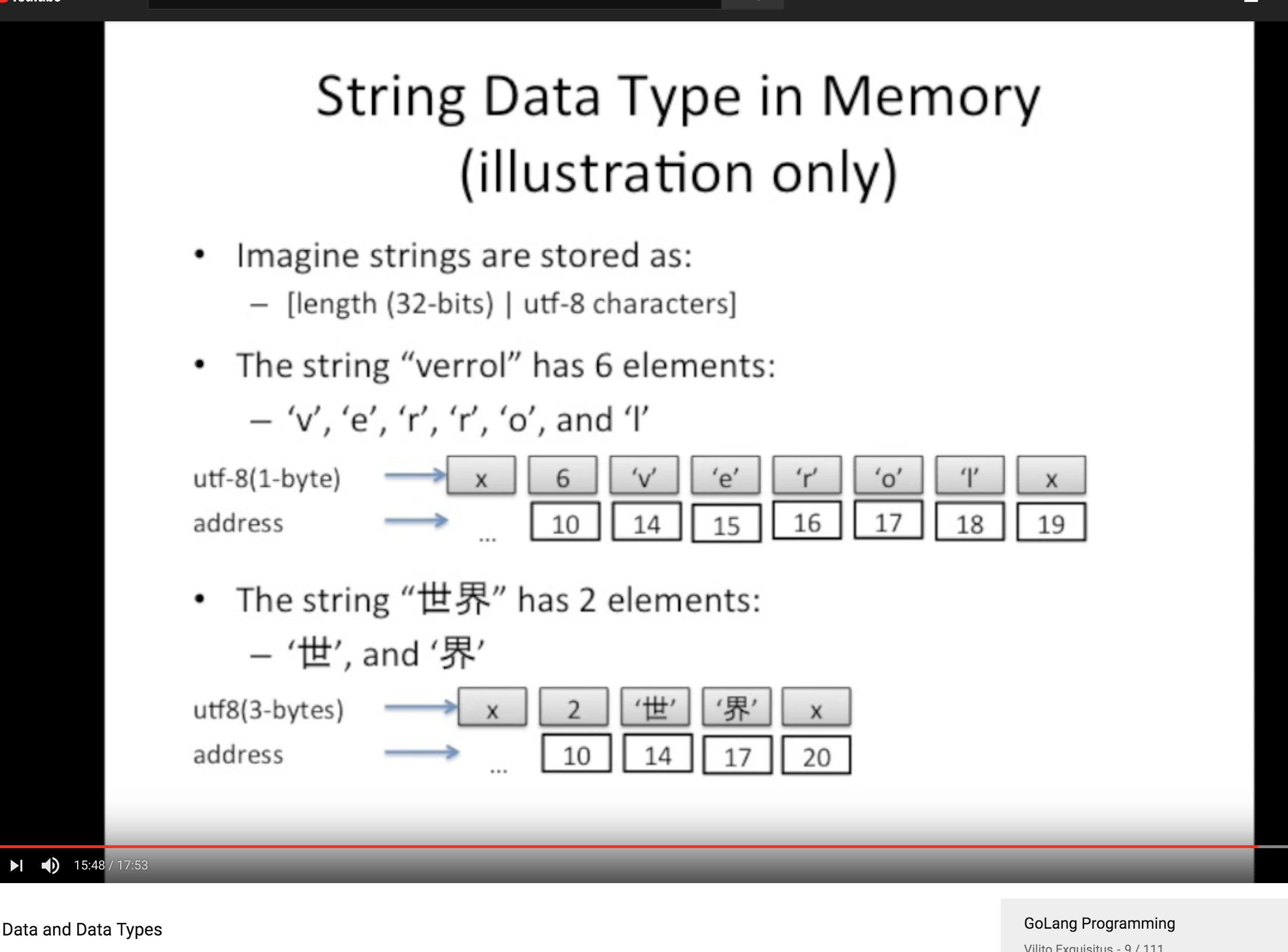
Constant
Constant

显式 vs 隐式类型
Constants & Variables

Pointers
Pointer

Address (reference)

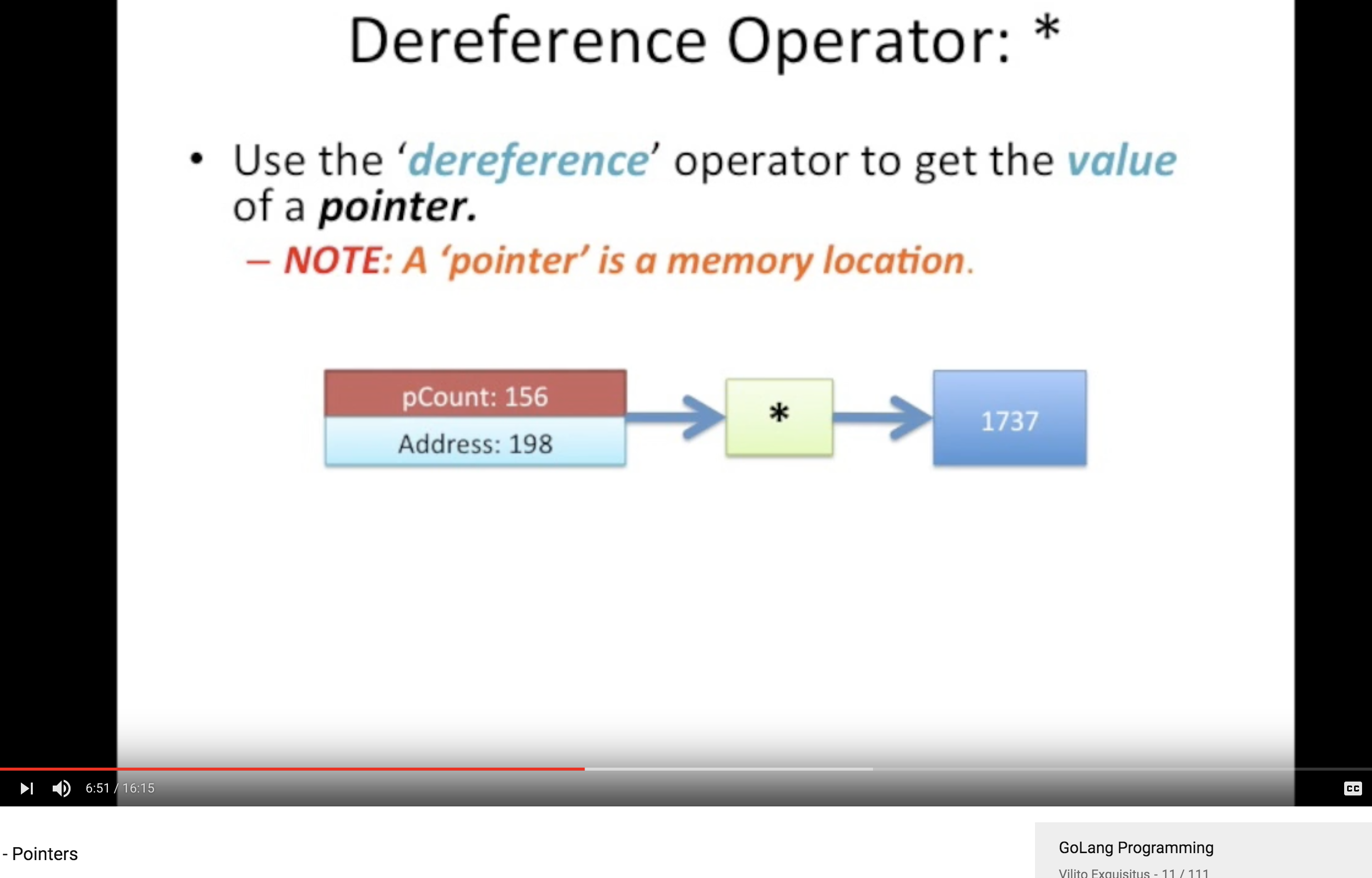
dereference
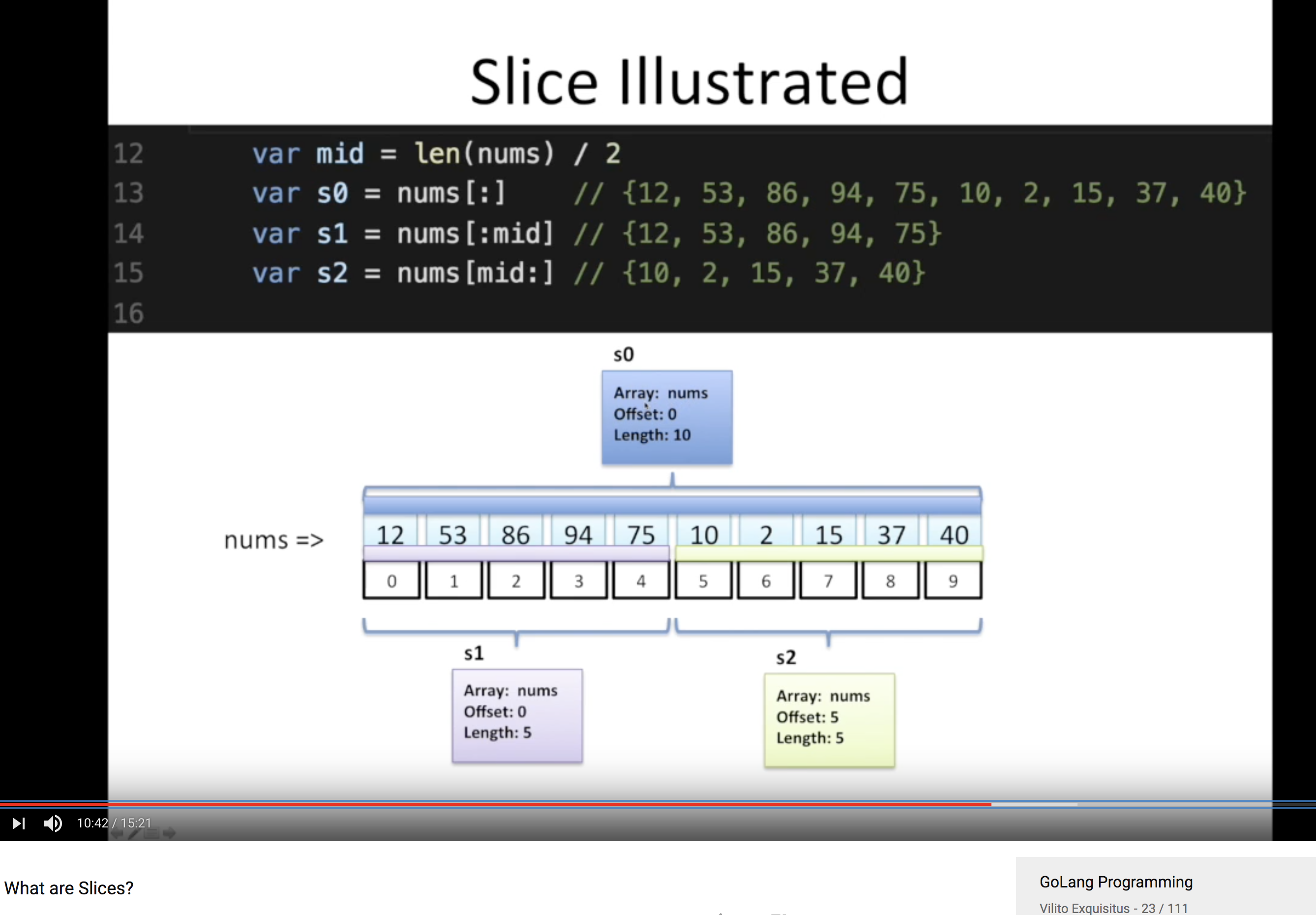
Slice
Slice
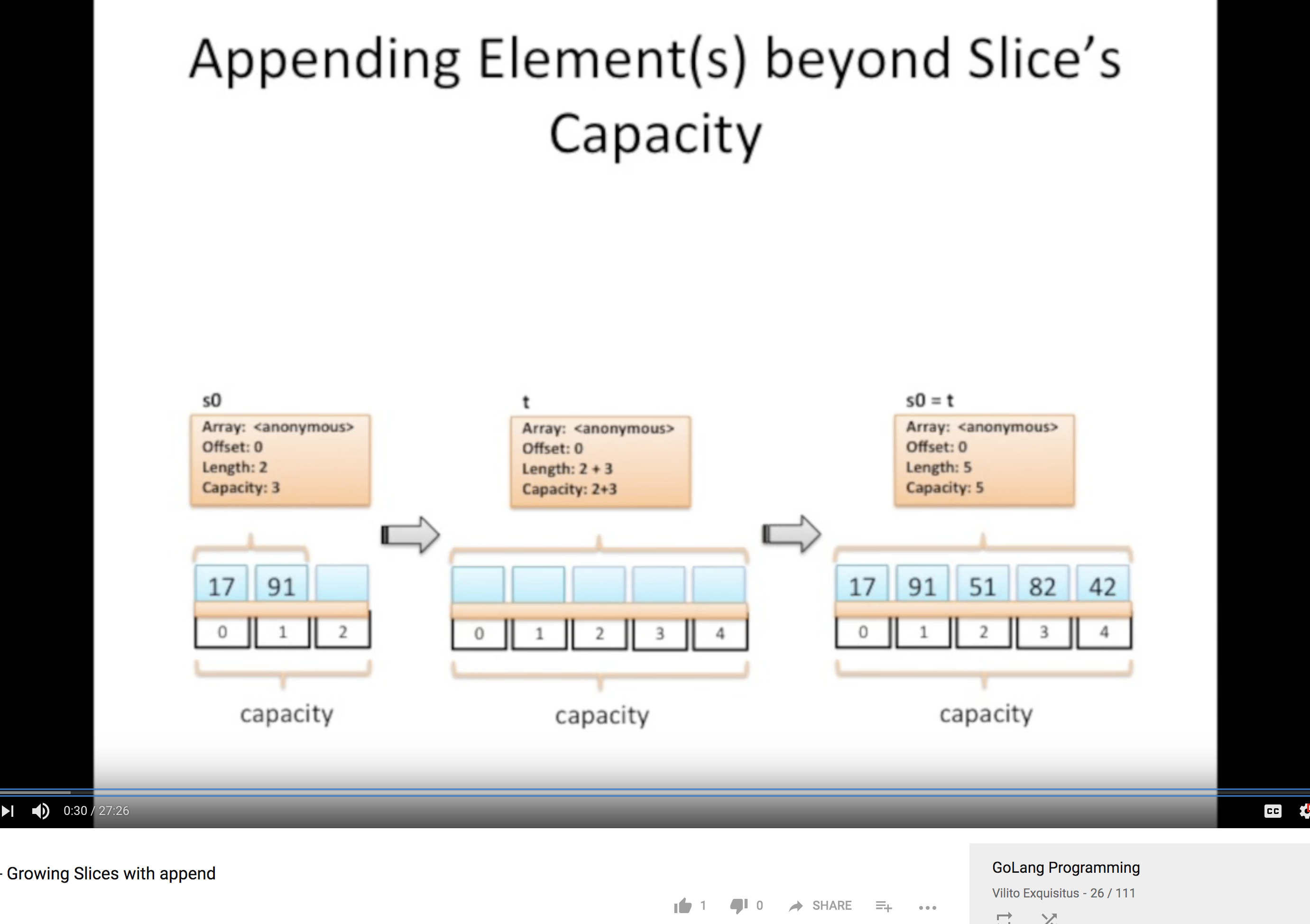
append
Map
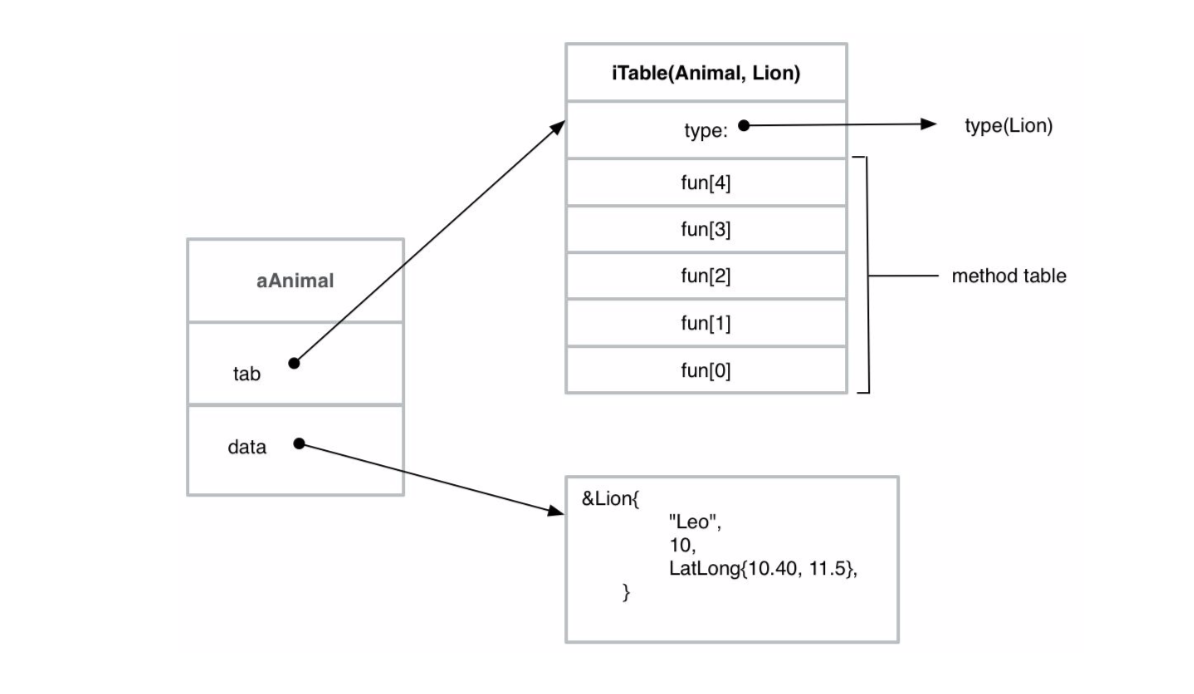
图解interface
定义 Animal interface

定义Lion实现Animal

实例

实例图解
Go Channel 操作状态及结果
| 操作 | 状态 | 结果 |
|---|---|---|
| 读 | nil | 阻塞 |
| 读 | 开启并不为空 | 获得对应值 |
| 读 | 开启并为空 | 阻塞 |
| 读 | 关闭 | 默认值, false |
| 读 | 只能写入 | 编译错误 |
| 写 | nil | 阻塞 |
| 写 | 开启并塞满 | 阻塞 |
| 写 | 开启并未塞满 | 写入对应值 |
| 写 | 关闭 | panic |
| 写 | 只能接收 | 编译错误 |
| 关闭 | nil | panic |
| 关闭 | 开启并不为空 | 关闭; 读取对应值直到 channel 为空, 之后读取时输出默认值 |
| 关闭 | 开启并为空 | 关闭; 读取时输出默认值 |
| 关闭 | 关闭 | panic |
| 关闭 | 只能接收 | 编译错误 |
YouTube推荐视频
Kavya Joshi - Understanding Channels
Liz Rice - A Go Programmer’s Guide to Syscalls
理解 goroutine
【编者的话】虽然已经有很多解释 goroutine 的优秀文章,但是对于初学者来说,大多都比较晦涩难懂,在这里总结一下自己对 goroutine 的理解以及相关资料
Goroutine
- Goroutine vs Thread - 推荐视频
Goroutines 既不是 OS 线程,也并非Green 线程
Goroutines 是更高层次的coroutines(协程)抽象
Goroutine 是并发的子程序(函数、闭包、方法),它们是 nonpreemptive(非抢占式的) - 不能被中断。相反,协程有多个可允许中断或重入的点。
Go 运行时观察 Goroutines 的状态,当阻塞时自动暂停它们,当它们非阻塞后又重新开启。这样 Goroutine 就是抢占式的协程,而且只有当它们阻塞时。
运行 goroutines 的机制是由 M:N 调度器实现的,该调度器将 M 个 green 线程映射到 N 个 OS 线上,然后将 Goroutines 调度到 green 线程上。
当 goroutines 多于可用的 green 线程,调度器将在可用的线程中处理 goroutines 的分布确保当某些 goroutines 阻塞时,其他的 goroutines 依然可以执行。
Work Stealing
- Work Stealing
- fair scheduling n 个处理器, x 个任务:每个处理器分配 x/n 个任务
Scheduler
- G go 协程
- M OS 线程(源代码中表示 machine)
- P context(源代码中表示 processor)
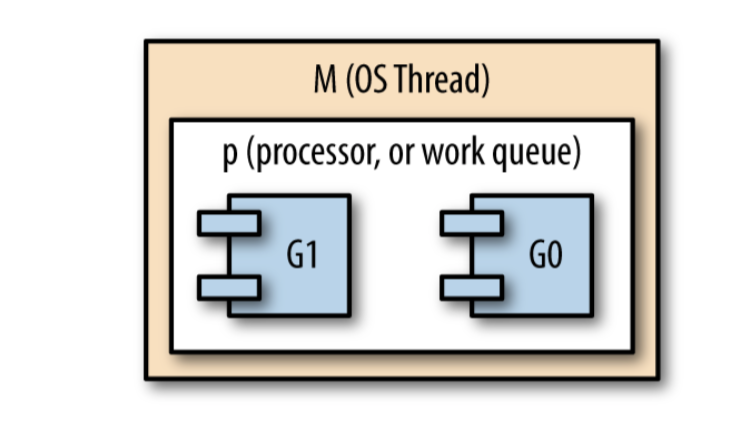
- GOMAXPROCS 控制着有多少 context 被用于运行时
<待续>
Issues
golang 应用使用 alpine 打包 Issue 总结:
Alpine linux doesn’t have nsswitch configuration file #367
golang http 默认请求 需要手动关闭
https://stackoverflow.com/a/41512208
It is the caller's responsibility to close Body.
coding 建议
- error 处理: 要么输出 log, 要么 return, 不要同时处理
- 用接口定义行为,不要用 data 或者 data 结构来定义
- 使用 io.Reader 和 io.Writer 接口,使你的 Go 代码更具可扩展性
- 确保传入的 function 的指针参数在需要时, 其他情况只需传入值
- Error 不是 string, 他们是 error
- 不要在 production 测试你的 Go 代码
- 不熟悉的 Go 语言的某些功能, 最好先测试一下,尤其是要开发一个应用或者大量用户会使用的工具
- 不要害怕出错, 尽可能多的尝试
机器学习
1. 数据组织 (数据收集/组织/解析)
CSV 数据处理 encoding/csv gota/dataframe
JSON 数据处理 encoding/json Go Walkthrough: encoding/json package
数据 VCS Pachyderm
2. 数据矩阵
- Vectors
<待续>
易错点
defer遵循LIFO(后进先出)原则 https://play.golang.org/p/kIqLpGJRjgidefer内有函数时,先计算再执行 https://play.golang.org/p/9T7lgXqxdyJfor range时&value不变 https://play.golang.org/p/lNma7BEAzsw
References:
